 Raman Proses Analizörü: Endüstriyel Süreç Kontrolünde Yenilik
Raman Proses Analizörü: Endüstriyel Süreç Kontrolünde Yenilik
 Bütün elmalardaki Brix derecelerinin gerçek zamanlı NIRS analizi
Bütün elmalardaki Brix derecelerinin gerçek zamanlı NIRS analizi

NIR spektroskopisi kullanılarak farmasötik formların kantitatif analizi

Visum Palm™ El Tipi NIR Analizörü - Farmasötik formların kantitatif analizi
Yakın kızılötesi spektroskopisi (NIRS), kapsamlı numune hazırlığına ihtiyaç duymadan hızlı, tahribatsız analiz yapabilme özelliği nedeniyle ilaç endüstrisinde önem kazanan analitik bir tekniktir. Visum Palm™ analizörü 900 nm ile 1700 nm arasındaki dalga boyu aralığını kapsar ve moleküler bağların titreşimlerinin üst tonları ve kombinasyonları nedeniyle enerji emilimi ile karakterize edilir.
Bu özellik, katı, sıvı veya toz farmasötik formülasyonlardaki aktif bileşenlerin ve yardımcı maddelerin miktarının belirlenmesinde özellikle yararlıdır ve içerik homojenliği, şüphesiz NIRS teknolojisinin bu sektördeki en ilgili uygulamalarından biridir ve belirli uygulamalardaki geleneksel analitik yöntemleri, Proses Analitik Teknolojileri veya PAT olarak adlandırılan yeni bir paradigma olan gerçek zamanlı proses izleme teknolojileriyle değiştirir veya tamamlar.
Visum Palm™ Analizör Serisi Hakkında - Farmasötik formların kantitatif analizi
Spektral 900 nm ila 1700 nm aralığı, çok yönlülük, olgunluk ve teknolojinin katı, toz ve özellikle sıvı formlarla çalışma yeteneği arasında en iyi dengeyi sunar. Visum Palm™ spektral aralığı, 1600 nm ila 2500 nm aralığında çalışan diğer analog cihazların aksine, daha düşük su emilim seviyeleri, daha iyi ışık penetrasyonu ve sonuç olarak daha düşük gürültü ile daha net, daha bilgilendirici bir sinyal sunar.
Visum Palm™ el tipi veya tezgah üstü (laboratuvar) analizörü


Geleneksel Analitik Yöntemler ve NIR Spektroskopisi
NIR teknolojisi, yüksek performanslı sıvı kromatografisi (HPLC), UV/Vis spektrofotometrisi, gaz kromatografisi veya kimyasal titrasyon yöntemleri gibi geleneksel analitik yöntemleri tamamlamak veya değiştirmek için idealdir.
Endüstride çok yaygın olan bir durum, farmasötik formlarda kuruma kaybının (LOD) belirlenmesi için Karl-Fischer yönteminin NIRS ile değiştirilmesidir. NIRS tekniğinin sunduğu bariz avantajlara rağmen (çok az numune hazırlama, reaktif gerektirmeme, anında sonuç alma ve proses parametrelerini düzeltme imkanı), çoğu durumda ve miktar belirleme uygulamasında miktar belirleme sınırı (LOQ) olan ağırlıkça %0,1 ila %1 aralığının altındaki konsantrasyonlarda aktif bileşenlerin (API’ler) veya yardımcı maddelerin miktarını belirlemek için aynı hassasiyete sahip olmadığını belirtmek gerekir.
Visum Palm™: Mevzuat Uyumluluğu
Visum Palm™ analiz cihazı ve yazılımı, Amerikan Farmakopesi (USP, 1119), Avrupa Farmakopesi (Ph. Eu., bölüm 2.2.40), FDA yönetmeliği 21 CFR Bölüm 11 ve Avrupa İlaç Ajansı (EMA) Kılavuzlarının tüm tavsiyelerine uyacak şekilde tasarlanmıştır: ‘Yakın kızılötesi spektroskopinin ilaç endüstrisi tarafından kullanımına ve yeni başvurular ve varyasyonlar için veri gerekliliklerine ilişkin kılavuz ‘ (2014), Ek ‘Bir NIRS Prosedürünün Kapsamının Tanımlanması ‘ (2023) ve ayrıca Aralık 2023 tarihli yeni ‘Analitik prosedür geliştirmeye ilişkin ICH Q14 Kılavuzu ‘.
- CFR uyumluluğu ve tüm cihaz kullanım bilgilerinin izlenebilirliği. Denetim İzi.
- Fotometrik dalga boyu, gürültü ve doğrusallığın doğrulanması. Analizörden yönlendirmeli sihirbaz. Otomatik cihaz durum raporlaması.
- Kendi kendine teşhis.
- Uzman bilgisi olmadan tanımlama, sınıflandırma ve miktar belirleme yöntemlerini geliştirme, güncelleme ve düzenleme yeteneği.
- Geliştirilen veya düzenlenen NIRS yöntemlerinin teknik bilgilerini içeren otomatik raporlar, iyileştirme ihtiyaçlarını tespit etmek, bakım planı veya validasyon dosyası için bilgi olarak.
- NIRS yöntemlerini çevrimdışı olarak harici numunelerle doğrulama imkanı.
- Tanımlama veya miktar belirleme analizi için kullanım raporlarının özelleştirilmesi.
- Kullanıcı ve izin yönetimi. “Analist”, “Süpervizör”, Kullanıcı Yöneticisi”.
Visum Palm™ el tipi analizör
Kantifikasyonda NIR Spektroskopisinin Faydaları
- Analiz hızı
NIR spektroskopisi, geleneksel yöntemlere kıyasla önemli ölçüde daha kısa analiz süreleri sunar. NIR analizi birkaç saniye içinde gerçekleştirilebilir ve üretim sırasında gerçek zamanlı kalite kontrolüne olanak sağlar.
- Tahribatsız analiz
Numunenin imha edilmesini gerektiren çoğu geleneksel yöntemin aksine, NIR spektroskopisi doğrudan tabletler, tozlar veya çözeltiler üzerinde onları rahatsız etmeden gerçekleştirilebilir ve gelecekteki analizler için daha yüksek numune verimine olanak tanır. Doğrudan yarı saydam torbaların içinden bile.
- Çok az veya hiç numune hazırlığı yok
NIR tekniği formülasyonun doğrudan analizine olanak tanıyarak çözündürme, filtreleme veya seyreltme gibi zahmetli numune hazırlama adımlarını ortadan kaldırır, böylece hata ve aşırı işlem riskini azaltır.
- Maliyet azaltma
Solvent, reaktif ve diğer sarf malzemelerine olan ihtiyacı ortadan kaldıran NIR tekniği, rutin analizlerle ilişkili maliyetleri önemli ölçüde azaltabilir. Buna ek olarak, otomasyon kolaylığı, gerekli manuel işçilik süresini azaltarak döngü sürelerini ve teslim süresini önemli ölçüde azaltır.
- Multiparametrik
NIR spektroskopisi, bir numune veya formülasyondaki birden fazla parametrenin eşzamanlı olarak ölçülmesini sağlar. Uygun şekilde kalibre edilmiş bir yöntemle, farklı API’lerin, yardımcı maddelerin ve hatta diğer özelliklerin konsantrasyonu tek bir analizde belirlenebilir.
- Üretim süreçlerine entegrasyon
NIR tekniği, süreç izleme sistemlerine (PAT) kolayca entegre edilerek üretim sırasında formülasyon özelliklerinin hat içi veya gerçek zamanlı kontrolüne olanak tanır ve böylece süreç verimliliğini artırır.
Visum Palm™ ile kantitatif bir yöntemin geliştirilmesi
Aşağıda, ‘X ‘ aktif bileşeninin %80 w/w hedef konsantrasyona sahip olduğu bir farmasötik formülasyonda miktar belirleme (içerik homojenliği testi) için Visum Palm™ analizörünün kullanıldığı bir örnek gösterilmektedir.
Bu amaçla, öngörücü modelin geliştirilmesi için sırasıyla %72 ve %96 arasında API konsantrasyonları açısından yeterli değişkenliğe sahip 20 kalibrasyon numunesi seti mevcuttu.
Aşağıda gösterildiği gibi Model Oluşturucu Visum Master™ , kalibrasyon ve dahili doğrulama numune setinin otomatik olarak 80/20 oranında bölünmesini sağlar.
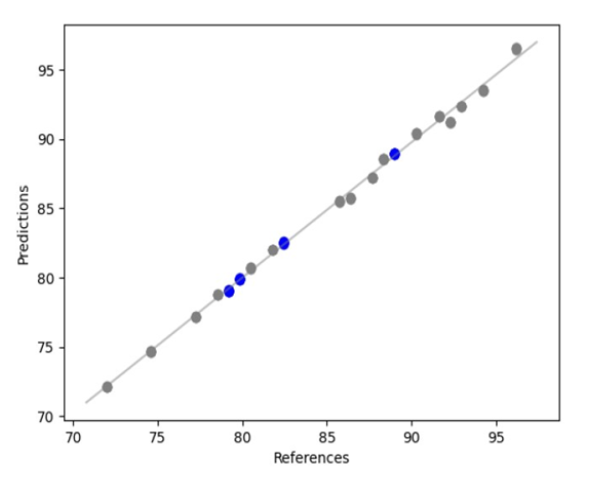
API ‘X’ regresyon eğrisi. Kalibrasyon veya modelleme numuneleri (gri) ve dahili doğrulama numuneleri (mavi).
Bir diğer önemli otomatik özellik, model uzayında bulunmayan spektrumlar olan aykırı değerlerin tespiti için otomatik bir kalite rutininin yürütülmesidir.
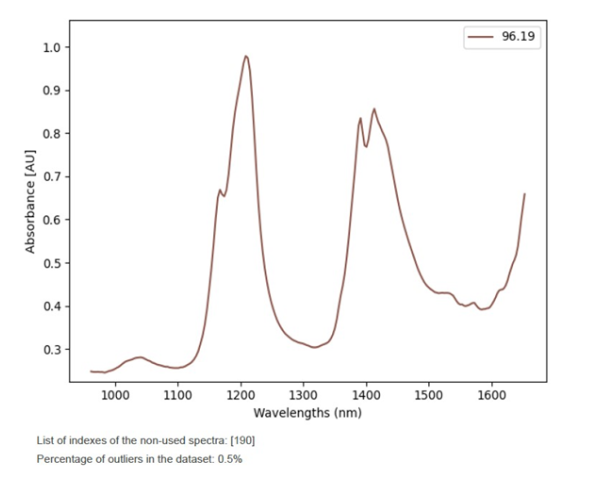
Visum Master™ yazılımı, modelleme setinde bulunan spektral aykırı değerleri çizer, tanımlar, ortadan kaldırır ve nicelleştirir. Bu durumda, girilen spektral bilgilerin kalitesinin iyi bir göstergesi olan %0,5’ten azdır.
Her durumda, %10’dan fazla aykırı değer tespit edilen bir modelin kullanılması tavsiye edilmez ve sonuç olarak numune hazırlama ve spektrum alma süreci gözden geçirilmelidir.
Tespit edilen ve modelleme örnek setinden çıkarılan aykırı değerler
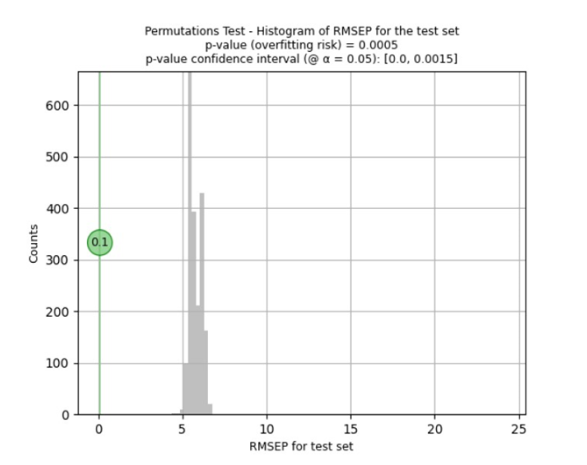
Aşırı uyum riskini, yani uygulanan ön işlemlerin ve ön işlemenin, yeni ve gelecekteki örneklerle çalışması gerekmeyen görünüşte iyi bir modelle sonuçlanmasını belirlemek için Visum Master™ yazılımı, gelecekteki örneklerle çalışma kalitesini sağlamak için Fisher-Pitman permütasyon testini çalıştırır.
Sonuçlar: NIR spektroskopisi kullanılarak farmasötik formların kantitatif analizi
API ‘X’in kantitatif tayini için elde edilen tahmin modeli 0,99’luk bir korelasyon katsayısı (R²) ve ± 0,1’lik bir Ortalama Karesel Tahmin Hatası (RMSEP) vermiştir.




